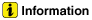Hyundai Santa Fe (TM): Cylinder Block
Hyundai Santa Fe (TM): Cylinder Block
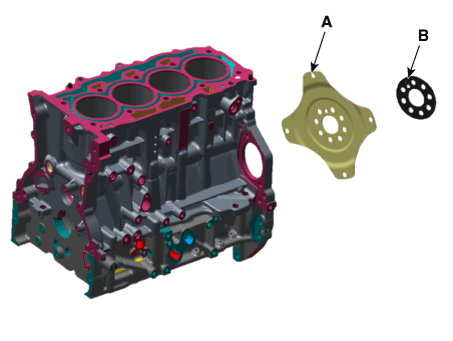
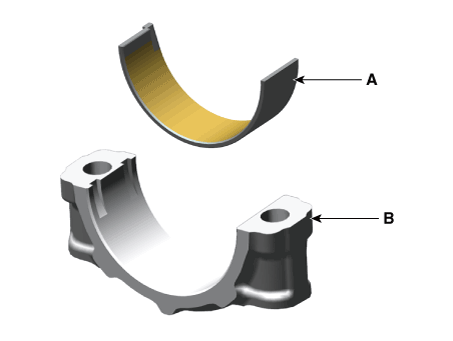
Drive Plate. Repair procedures
| Removal and Installation |
|
| 1. |
Remove the automatic transaxle .
(Refer to Automatic Transaxle System - "Automatic Transaxle")
|
| 2. |
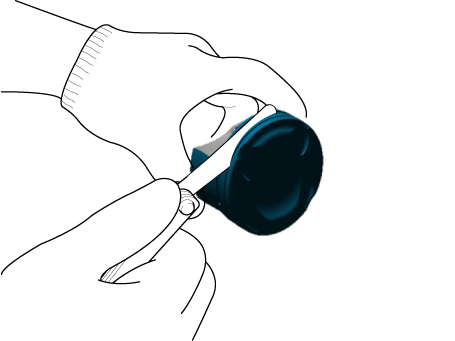
Remove the drive plate (A) and the adapter plate (B).
|
| 3. |
Install in the reverse order of removal.
|
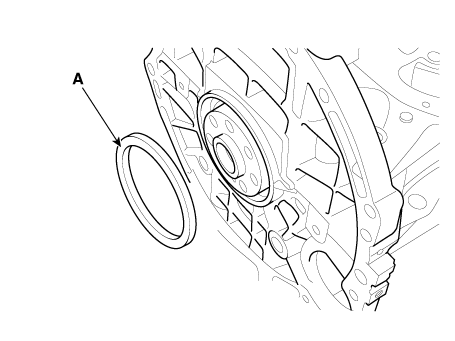
Rear Oil Seal. Repair procedures
| Removal |
|
| 1. |
Remove the automatic transaxle.
(Refer to Automatic Transaxle System - "Automatic Transaxle")
|
| 2. |
Remove the drive plate.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Drive Plate")
|
| 3. |
Rmove the rear oil sela (A).
|
| Installation |
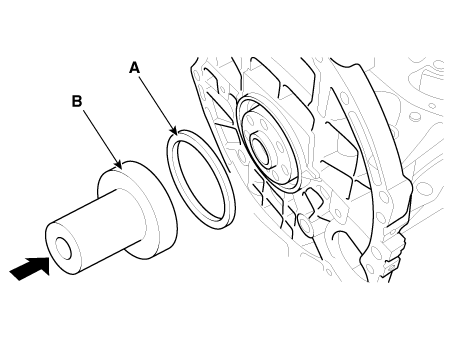
| 1. |
Install rear oil seal.
|
| 2. |
Install the drive plate.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Drive Plate")
|
| 3. |
Install the automatic transaxle.
(Refer to Automatic Transaxle System - "Automatic Transaxle")
|
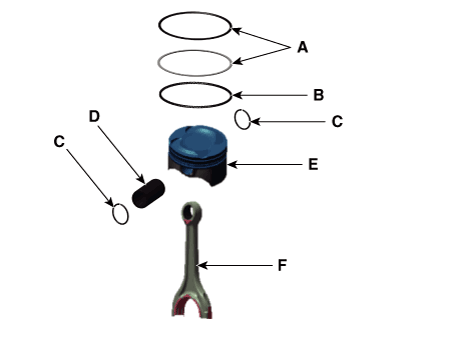
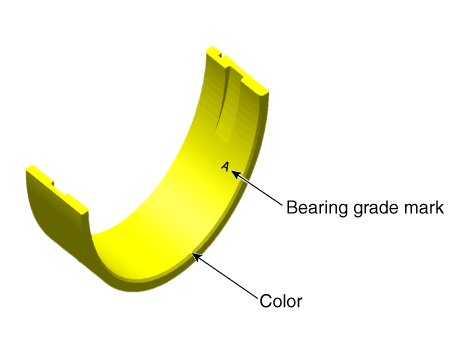
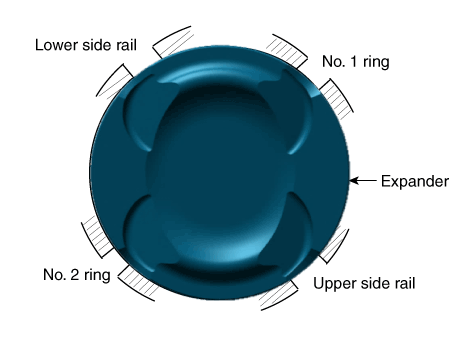
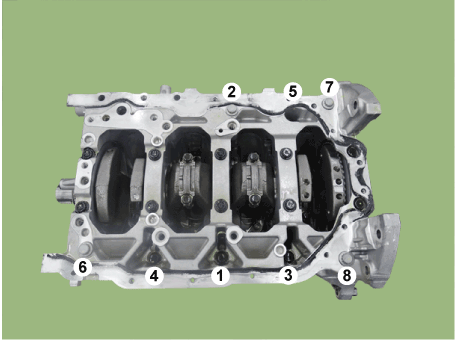
Piston and Connecting Rod. Components and components location
| Components |
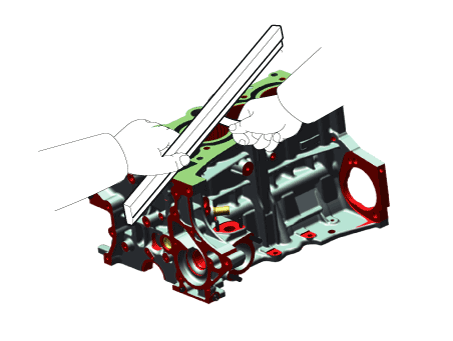
| 1. Piston ring 2. Snap ring 3. Piston 4. Connecting rod |
5. Connecting
rod upper bearing 6. Connecting rod lower bearing 7. Connecting rod bearing cap |
Piston and Connecting Rod. Repair procedures
| Disassembly |
|
|
|
| 1. |
Remove the engine and transaxle assembly.
(Refer to Engine and Transaxle Assembly - "Engine and Transaxle Assembly")
|
| 2. |
Remove the harness clamp from the wiring connector around the engine
and transaxle and remove the connector bracket.
|
| 3. |
Remove the automatic transaxle .
(Refer to Automatic Transaxle System - "Automatic Transaxle")
|
| 4. |
Remove the drive plate.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Drive Plate")
|
| 5. |
Remove the rear oil seal.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Rear Oil Seal")
|
| 6. |
Install the engine assembly to engine stand for disassembly.
|
| 7. |
Remove the oil pan.
(Refer to Lubrication System - "Oil Pan")
|
| 8. |
Remove the timing chain.
(Refer to Timing System - "Timing Chain")
|
| 9. |
Remove the intake manifold.
(Refer to Intake and Exhaust System - "Intake Manifold")
|
| 10. |
Remove the exhaust manifold.
(Refer to Intake and Exhaust System - "Exhaust Manifold")
|
| 11. |
Remove the cylinder head.
(Refer to Cylinder Head Assembly - "Cylinder Head")
|
| 12. |
Remove the water jacket insert.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Water Jacket Insert")
|
| 13. |
Remove the oil cooler & filter.
(Refer to Lubrication System - "Oil Cooler & Filter")
|
| 14. |
Remove the alternator.
(Refer to Engine Electrical System - "Alternator")
|
| 15. |
Remove the A/C compressor.
(Refer to Heateng, Ventilation, Air conditioning - "Compressor")
|
| 16. |
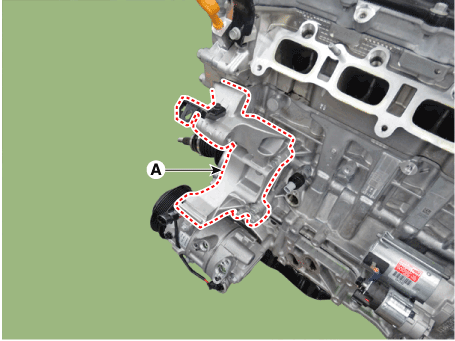
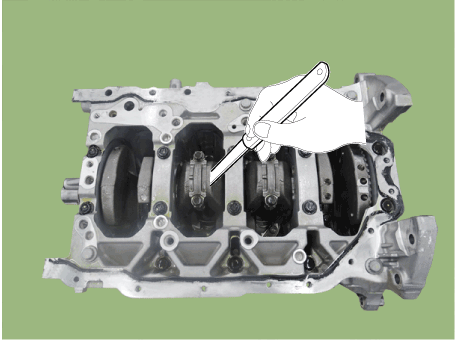
Remove the tensioner assembly integrated bracket (A).
|
| 17. |
Remove the oil pump.
(Refer to Lubrication System - "Oil Pump")
|
| 18. |
Remove the balance shaft module.
(Refer to Lubrication system - "Balance Shaft Module")
|
| 19. |
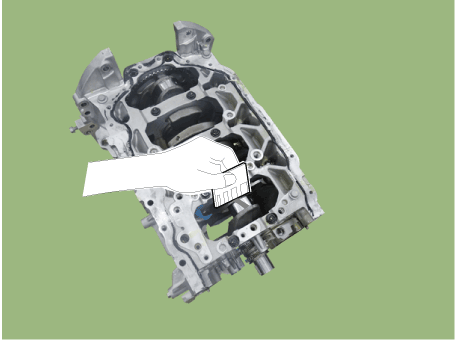
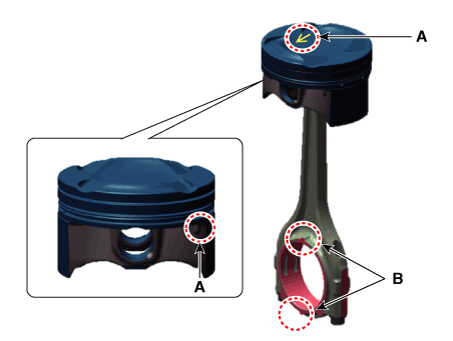
Remove the piston and connecting rod assembly.
|
| 20. |
Check fit between piston and piston pin.
Try to move the piston back and forth on the piston pin. If any movement
is felt, replace the piston and piston pin as a set.
|
| 21. |
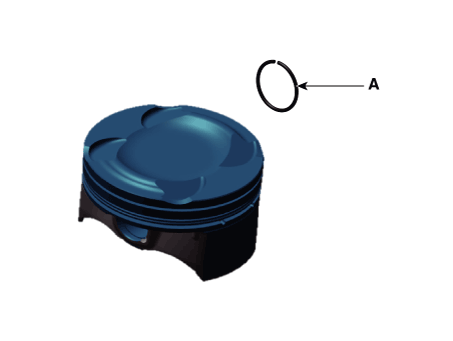
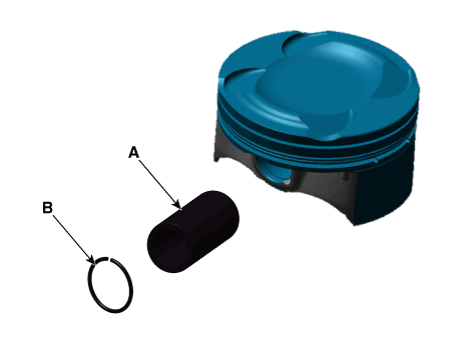
Disassemble the piston rings.
|
| 22. |
Disassemble the connecting rod from the piston.
|
| Inspection |
| 1. |
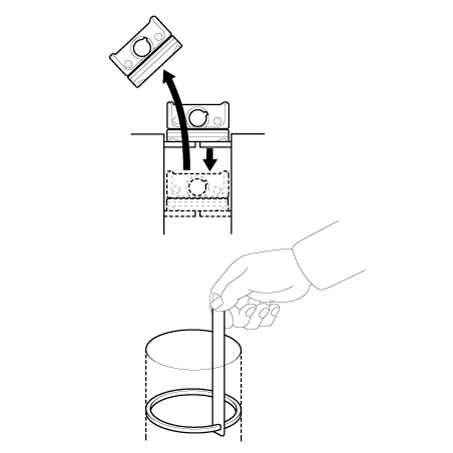
Check the connecting rod end play.
Using a feeler gauge, measure the end play while moving the connecting
rod back and forth.
|
| 2. |
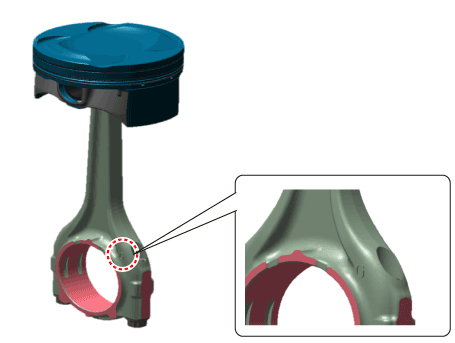
Check the connecting road bearing oil clearance.
|
| 3. |
Inspect the connecting rods.
|
| 1. |
Clean piston
|
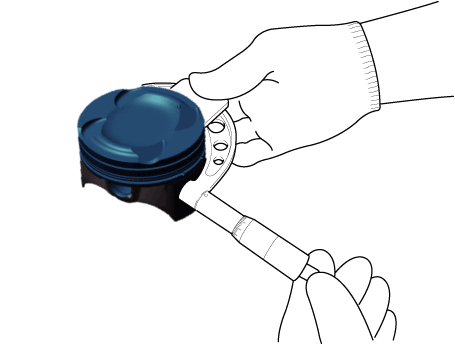
| 2. |
Check the piston-to-cylinder clearance by calculating the difference
between the cylinder bore inner diameter and the piston outer diameter.
|
| 3. |
Select the piston matching with cylinder bore class.
|
| 1. |
Inspect the piston ring side clearance.
Using a feeler gauge, measure the clearance between new piston ring
and the wall of ring groove.
|
| 2. |
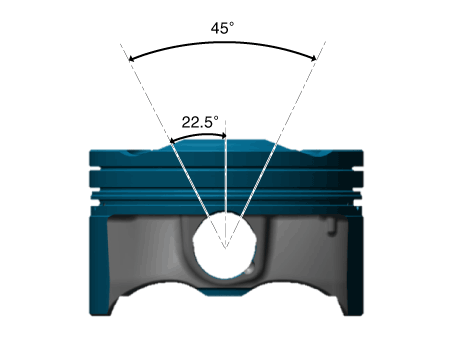
Inspect the piston ring end gap.
To measure the piston ring end gap, insert a piston ring into the cylinder
bore. Position the ring at right angles to the cylinder wall by gently
pressing it down with a piston. Measure the gap with a feeler gauge.
If the gap exceeds the specifications, replace the piston rings. If
the gap is too large, recheck the cylinder bore inner diameter.
|
| 1. |
Measure the diameter of the piston pin.
|
| 2. |
Measure the piston pin-to-piston clearance.
|
| 3. |
Check the difference between the piston pin diameter and the connecting
rod bushing oil clearance.
|
| Reassembly |
|
| 1. |
Assemble the piston and the connecting rod.
|
| 2. |
Install the piston rings.
|
| 3. |
Install the connecting rod bearings.
|
| 4. |
Install the piston and connecting rod assembly.
|
| 5. |
Assemble the other parts in the reverse order of disassembly.
|
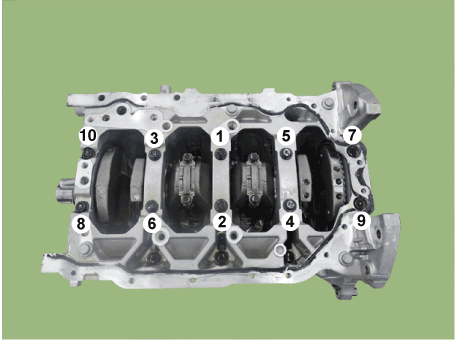
Crankshaft. Components and components location
| Components |
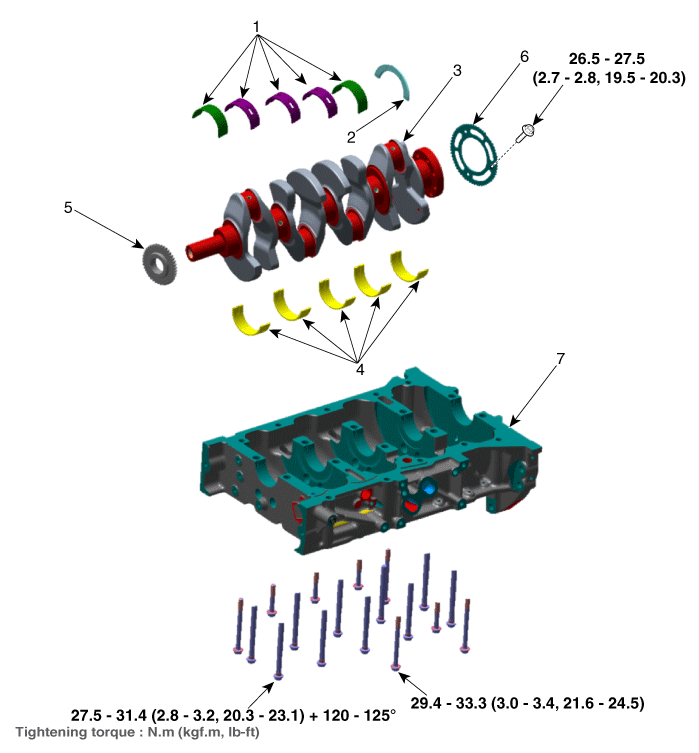
| 1. Crankshaft
upper bearing 2. Thrust bearing 3. Crankshaft 4. Crankshaft lower bearing |
5. Crankshaft
sprocket 6. Crankshaft position sensor wheel 7. Lower crankcase |
Crankshaft. Repair procedures
| Disassembly |
|
|
|
| 1. |
Remove piston and connecting rod assemblies.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Piston and Connecting Rod")
|
| 2. |
Remove the lower crankcase.
|
| 3. |
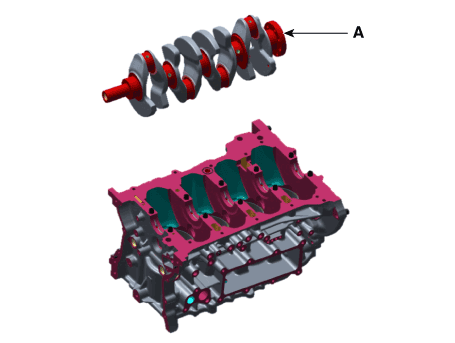
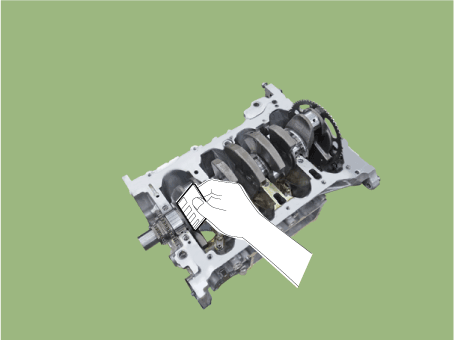
Lift the crankshaft (A) out of the engine block, be careful not to damage
journals.
|
| 4. |
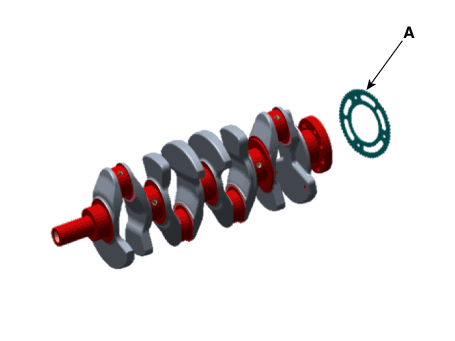
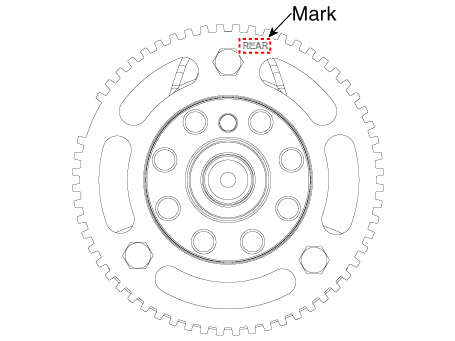
Remove the crankshaft position sensor wheel (A).
|
| Inspection |
| 1. |
Check the crankshaft bearing oil clearance.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. |
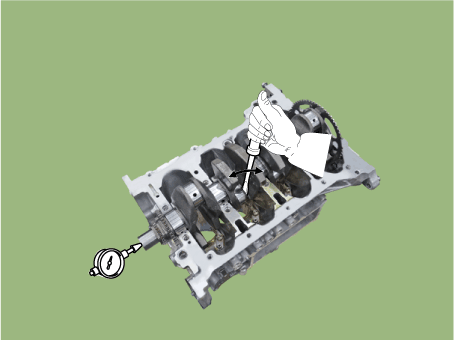
Check the crankshaft end play.
Using a dial indicator, measure the thrust clearance while prying the
crankshaft back and forth with a screwdriver.
If the end play is greater than maximum, replace the thrust bearings
as a set.
|
| 3. |
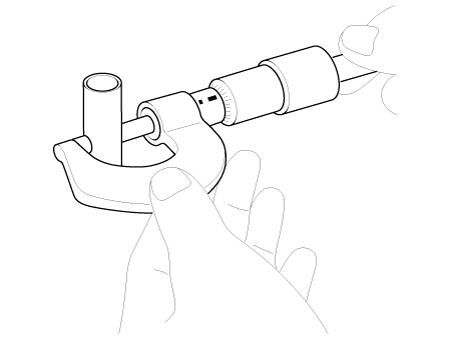
Inspect the crankshaft main journals and pin journals.
Using a micrometer, measure the diameter of each main journal and pin
journal.
|
| Reassembly |
|
| 1. |
Install the crankshaft position sensor wheel (A).
|
| 2. |
Install the main bearing.
|
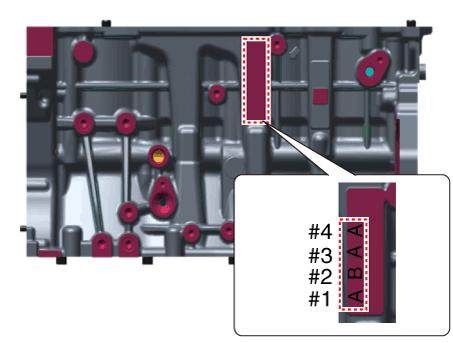
| 3. |
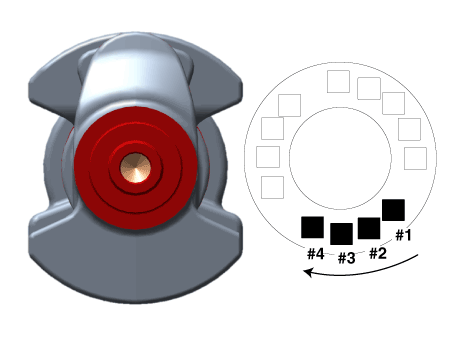
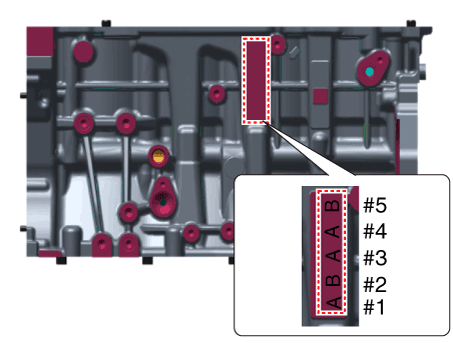
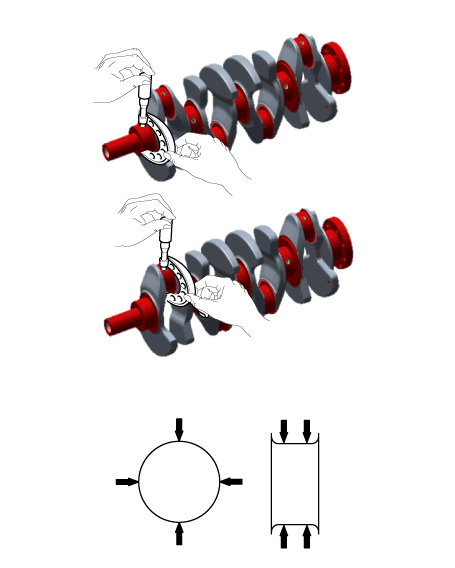
Install the thrust bearings.
Install the 2 thrust bearings (A) on both sides of the No.4 journal
of the cylinder block with the oil groove facing out.
|
| 4. |
Install the crankshaft (A) on the cylinder block.
|
| 5. |
Install the lower crankcase.
|
| 6. |
Check the crankshaft end play.
|
| 7. |
Install the piston and connecting rod assemblies.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Piston and Connecting Rod")
|
| 8. |
Assemble the other parts in the reverse order of disassembly.
|
Cylinder Block. Repair procedures
| Disassembly |
|
|
|
| 1. |
Remove the crankshaft.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Crankshaft")
|
| 2. |
Remove the knock sensor.
(Refer to Engine Control / Fuel System - "Knock Sensor (KS)")
|
| 3. |
Remove the crankshaft position sensor (CKPS).
(Refer to Engine Control / Fuel System - "Crankshaft Position Sensor
(CKPS)")
|
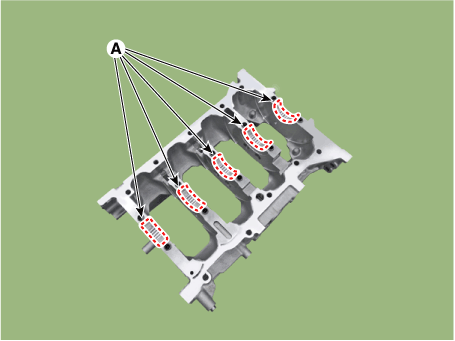
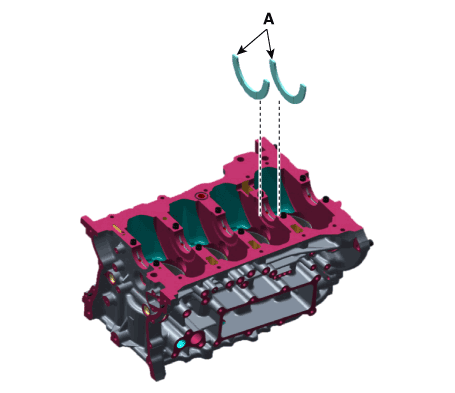
| 4. |
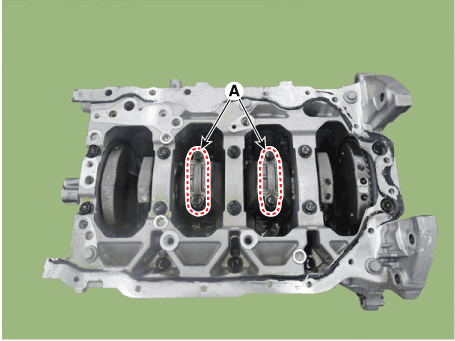
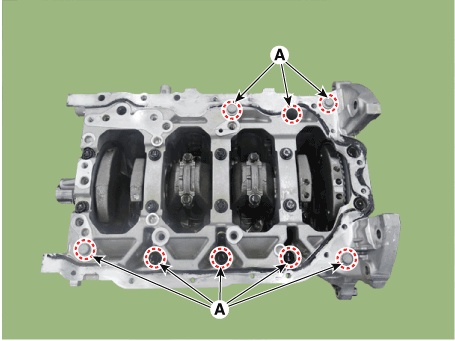
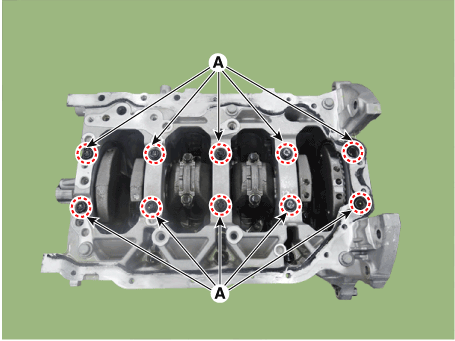
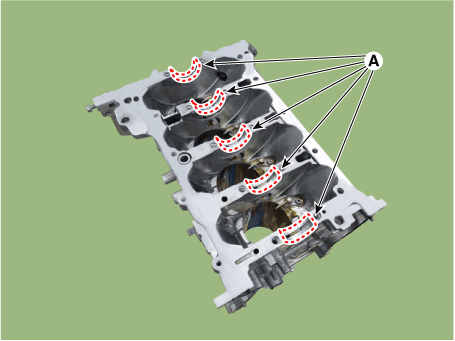
Remove the piston cooling oil jets (A).
|
| Inspection |
| 1. |
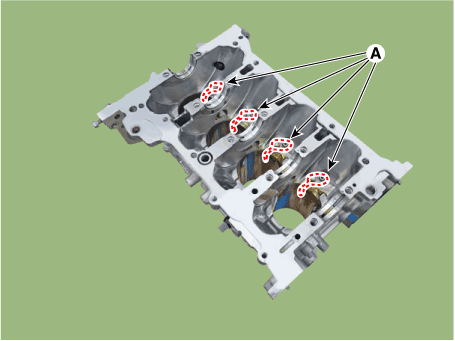
Using a gasket scraper, remove all the gasket material from the top
surface of the cylinder block.
|
| 2. |
Using a soft brush and solvent, thoroughly clean the cylinder block.
|
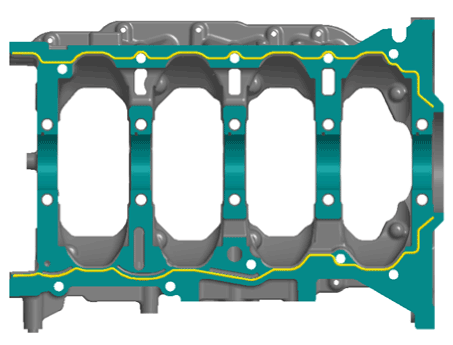
| 3. |
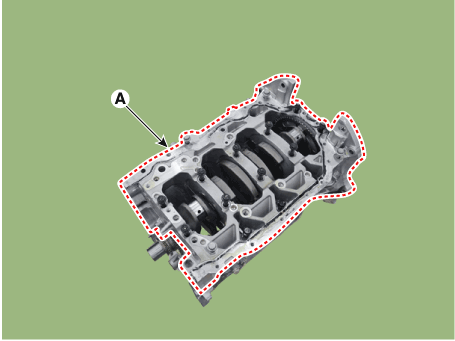
Inspect the top surface of cylinder block for flatness.
Using a precision straight edge and feeler gauge, measure the surface
contacting the cylinder head gasket for warpage.
|
| 4. |
Visually check for scratches on the inside surface of the cylinder bore
and replace the cylinder block if any noticeable scratch is detected.
If deep scratchs are present, replace the cylinder block.
|
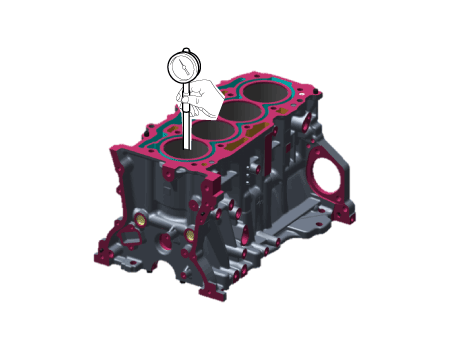
| 5. |
Using the cylinder bore gauge, measure the cylinder bore’s inner diameter
to the axial and axial perpendicular directions.
|
| Reassembly |
|
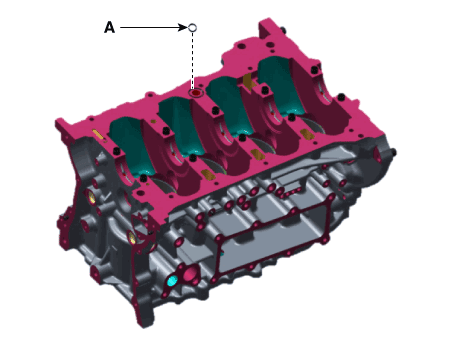
| 1. |
Install the piston cooling oil jets (A).
|
| 2. |
Install the crankshaft.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Crankshaft")
|
| 3. |
Check the crankshaft end play.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Crankshaft")
|
| 4. |
Disconnect the lower crankcase and check crankshaft bearing oil clearance.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Crankshaft")
|
| 5. |
Install the piston and connecting rod assembly.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Piston and Connecting Rod")
|
| 6. |
Check the connecting rod bearing cap oil clearance.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Piston and Connecting Rod")
|
| 7. |
Check the connecting rod end play.
(Refer to Cylinder Block - "Piston and Connecting Rod")
|
| 8. |
Assemble the other parts in the reverse order of disassembly.
|
 Cylinder Head Assembly
Cylinder Head Assembly
Components and components location Components 1. Camshaft front bearing cap 2. Camshaft bearing cap 3. OCV & Center bolt 4. Exhaust CVVT assembly 5. Exhaust camshaft 6. Intake camshaft 7. Intake CVVT ...
 Cooling System
Cooling System
Coolant. Repair procedures Refilling And Bleeding • Never remove the reservoir tank cap when the engine is hot. Serious scalding could be caused by hot fluid under high pressure escaping ...
See also:
Tail Gate Weatherstrip. Repair procedures
Replacement 1. Remove the tail gate weatherstrip (A). • Do not apply sealant to the body. 2. Install in the reverse order of removal. • Install the weatherstrip aligned with canter line (B). ...
Seat belts - Front passenger and rear seat 3-point system with combination locking
retractor
To fasten your seat belt: Combination retractor type seat belts are installed in the rear seat positions to help accommodate the installation of child restraint systems. Although a combination retractor ...
Catalytic Converter. Description and Operation
Description The catalytic converter of the gasoline engine is a three way catalyst. It oxidizes carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons (HC), and separates oxygen from the oxides of nitrogen (NOx). [WCC] [UCC] ...